GenAI has its points. But when there’s one factor it excels at, it’s surfacing solutions from huge swimming pools of information.
Enter Glean, whose software program connects to enterprise first- and third-party databases to subject plain-English requests (e.g. “How do I put money into our firm’s 401k?”) from workers, type of like a customized ChatGPT. Launched by Arvind Jain, the co-founder of cloud information administration firm Rubrik, Glean was impressed by Jain’s observations that Rubrik workers usually struggled to seek out the knowledge they wanted to do their jobs — and that staffers at different corporations had been scuffling with the identical.
“I noticed that engineers had been spending an excessive amount of time outdoors code, account managers couldn’t discover the newest analysis or presentation wanted to shut offers, new workers took too lengthy to onboard, and so forth” Jain instructed TechCrunch in an interview. “This rising downside destroyed productiveness, sapped power and detracted from the worker expertise.”
It appears Jain was onto one thing.
A latest Gartner survey discovered that 47% of desk staff have bother discovering the info they should carry out their jobs. In the identical survey, staff reported that the rising variety of apps they must handle at work — 11 on common now versus six 5 years in the past — is exacerbating the problem.
In 2019, Jain — together with a small founding group — constructed Glean as an AI-powered search app geared towards enterprise clients.
The primary few iterations had been alongside the strains of Microsoft’s SharePoint Syntex and Amazon Kendra, occupying a product class often known as “cognitive search.” Utilizing pure language processing, the early Glean might perceive doc minutia along with searches workers throughout a company may carry out.
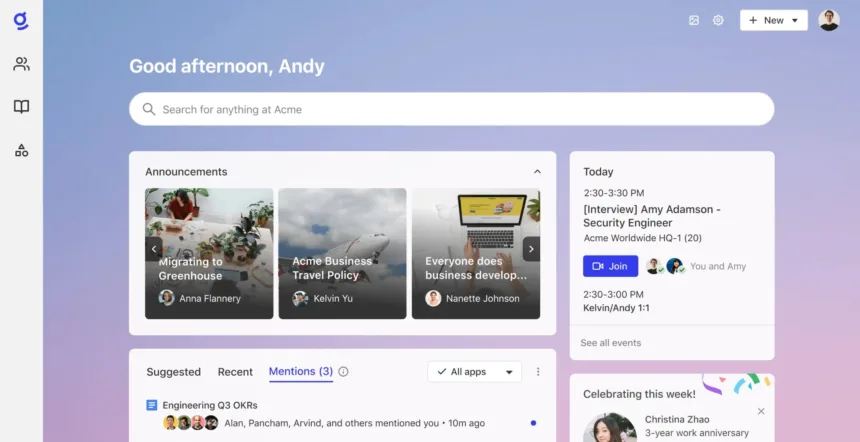
Picture Credit: Glean
Over time, Glean advanced right into a platform that connects with and analyzes an organization’s databases and information shops to reply worker inquiries — following after the explosive GenAI development. Glean in the present day ingests information from sources together with help tickets, chat messages and buyer relationship administration platform entries and applies GenAI to try to show that each one that into insights and related solutions.
One imagines corporations can be cautious of connecting their proprietary information — particularly their inner chat information — to a GenAI platform that performs this deep a degree of scraping and evaluation. And that wouldn’t be an incorrect assumption.
A latest Cisco poll discovered that multiple in 4 organizations have banned using GenAI over privateness and information safety dangers. Within the ballot, corporations stated they feared GenAI instruments would compromise their IP or probably disclose different delicate data to the general public — or their rivals.
However Jain asserts that Glean is “safe” and “non-public” — not less than to the extent a cloud-based GenAI platform can be.
“Glean respects the identical permissions set in an organization’s information sources (Slack, Groups, Jira, ServiceNow, and so forth.), so workers solely obtain solutions primarily based on the info they’re allowed to entry,” Jain stated. “When a person deletes a doc within the underlying software, the doc will get deleted from the Glean system.”
What in regards to the curse from which most GenAI suffers, although — hallucinations? Is Glean immune from making up information and citations, getting summaries improper and lacking the purpose of fundamental requests?
It’s potential; this author wasn’t capable of take a look at Glean himself. However Jain, whereas neither confirming nor denying Glean hallucinates, highlighted the mitigations in place to make the platform’s GenAI extra dependable. together with a mannequin skilled on buyer information to be taught trade and firm-specific jargon and letting clients change amongst a number of open supply GenAI fashions to drive Glean’s core expertise.
“AI work assistants have to ship personalised outcomes primarily based on who’s looking,” Jain stated. “Varied facets of the searcher — their position, job perform, administration hierarchy, particular initiatives and tasks and even who they work with — find yourself being vital in defining the content material that’s related to them. Glean learns a customized mannequin for each buyer to ship extremely personalised outcomes to each worker primarily based on these attributes.”
Glean additionally employs RAG (quick for Retrieval-Augmented Technology), an more and more widespread method used to “floor” GenAI by retrieving information from outdoors sources of information, to spice up efficiency. Jain says that each reply Glean offers is “totally referenceable” again to the unique supply.
“Glean [can recommend the] paperwork customers may want for his or her day-to-day work by studying from previous work patterns,” Jain stated. “[It] delivers turnkey implementation of a fancy AI ‘ecosystem,’ with over 100 connectors.”
Glean makes cash by charging a month-to-month per-seat subscription, primarily based on annual contracts.
Regardless of competitors from distributors like Microsoft (particularly Copilot) and OpenAI (ChatGPT) in addition to enterprise search suppliers similar to Coveo, Sinequa and Lucidworks, Jain says that enterprise has been fairly sturdy as of late, with annual recurring income near quadrupling within the final 12 months.

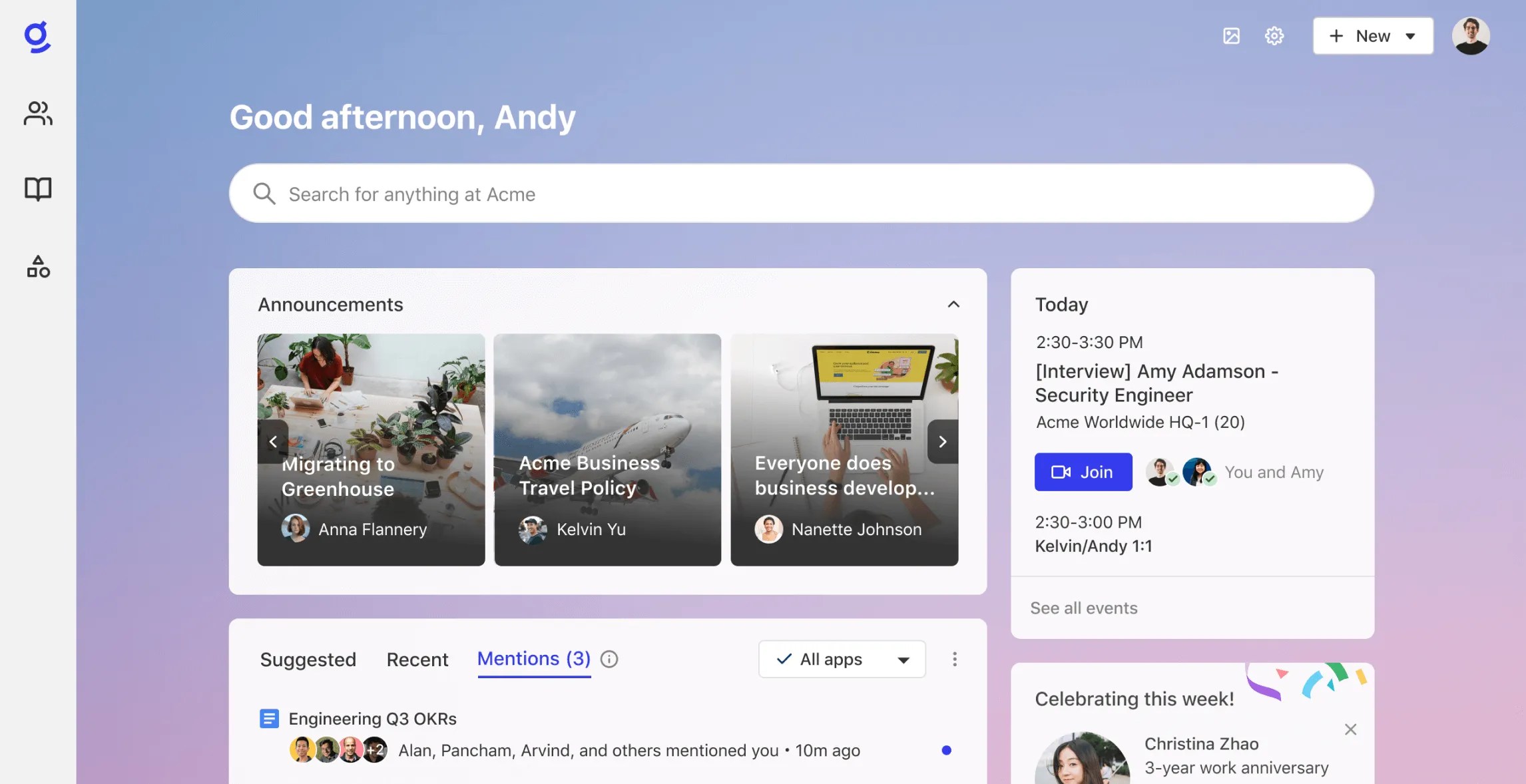
Picture Credit: Glean
That runs counter to the narrative that companies — removed from embracing GenAI wholeheartedly — have been sluggish and cautious to deploy it throughout their enterprise capabilities.
Responding to a December 2023 survey by Convrg.io, the Intel subsidiary, solely 10% of organizations stated that they’d launched GenAI options all the best way to manufacturing in 2023. The overwhelming majority of options remained within the analysis and testing phases, the organizations stated — implying corporations haven’t been profitable find money-making GenAI use circumstances.
Glean’s financials — and a 200-strong buyer base that features Duolingo, Grammarly and Sony — seem to have gained over buyers, nevertheless.
Glean in the present day introduced that it raised $200 in a Sequence D funding spherical co-led by Kleiner Perkins and Lightspeed Enterprise Companions with participation from Normal Catalyst, Sequoia Capital, Adams Avenue, Coatue, ICONIQ, IVP, Latitude Capital and extra strategic backers Capital One Ventures, Citi Ventures, Databricks Ventures and Workday Ventures.
Kleiner Perkins’ Mamoon Hamid had this to say in a press release: “The chance for Glean is big, and we now have a lot conviction within the group’s skill to offer the GenAI answer for the enterprise that we co-led this spherical after investing in each spherical previous to this, after main their Sequence A in 2019. I’ve spent my enterprise profession investing in purposes that allow information staff to be extra productive, whether or not it’s Slack, Field or Figma, and see large potential in Glean to vary the best way that folks work.”
Jain says that the brand new capital, which brings Glean’s whole raised to $358 million and values the startup at $2.2 billion, shall be put towards increasing “all of” Glean’s groups (the San Francisco-based firm has ~300 workers at current), enhancing its product and “constructing out a strong go-to-market movement.”
“Glean has continued to see sturdy and rising buyer demand, particularly from enterprises who’ve spent the previous 12 months evaluating the required necessities to deliver GenAI into their organizations,” Jain stated. “We’ve at all times been prudent in hiring and spending, and the latest improve in hiring is to fulfill sturdy buyer demand.”