While you add and handle your knowledge on GitHub that nobody else can see until you make it public, you share bodily infrastructure with different customers. That is as a result of GitHub makes use of multitenancy as an economical and easier-to-manage different to assigning a separate database to every person.
Nonetheless, sharing the identical infrastructure turns into a safety threat when all customers can view one another’s knowledge. Multitenancy addresses this problem by logically partitioning person knowledge whereas permitting them to run on the identical assets.
This text explores multitenancy in vector databases, its advantages, limitations, and real-world use instances.
How Does Multitenancy Work in Vector Databases?
Multitenancy is an method the place a number of tenants, i.e., customers, share the identical database however retailer their knowledge in an remoted setting.
An remoted setting is created utilizing distinctive credentials for every tenant to safe their knowledge. In consequence, every tenant can retailer, handle, and alter their knowledge of their remoted setting. Nonetheless, the corporate has the entry to handle and management tenant assets and limitations.

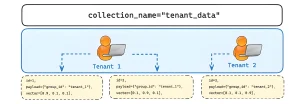
Pattern illustration of a two-tenant assortment with remoted entry to the identical database. Picture Supply: Qdrant
Vector databases use indexing as a search method that organizes vectors primarily based on similarity. The indexing technique impacts the tenant knowledge partitioning. At present, two indexing methods are utilized in multitenant vector databases.
Let’s focus on each indexing methods in multitenant vector databases:
- Shared Indexing: All tenants share the identical index with distinctive credentials partitioning the info. This technique is reminiscence environment friendly. Nonetheless, it requires strong safety and entry management mechanisms to guard tenant knowledge.
- Per-tenant Indexing: Each tenant has a separate index in per-tenant indexing. This permits full entry management and improved search efficiency. Nonetheless, this technique is resource-intensive.
Some vector databases like Qdrant and Milvus supply multitenant structure to permit added customization and scalability for customers with each indexing methods.
Advantages of Multitenancy in Vector Databases
Multitenancy in vector databases affords quite a few advantages for corporations that require remoted database cases for a number of customers. Among the advantages embody:
1. Value discount
Utilizing fewer assets for extra customers leads to decreased infrastructure prices.
2. Scalability
Multitenancy permits need-based useful resource sharing. This implies tenants with extra storage necessities get extra assets and vice versa.
3. Customization
A separate setting permits tenants to configure it primarily based on their wants, together with database schema, plugins, metrics, and dashboards. Configurations are personal to tenants, and tenants can change them as their necessities change.
4. Manageability
A single database for all tenants permits centralized resource management, configuration, and monitoring as an alternative of monitoring all tenants individually. Whereas an organization can handle all tenants in a single place, tenants have the management to handle their knowledge inside their remoted environments.
Limitations of Multitenancy in Vector Databases
Like some other architectural method, multitenancy has some limitations. Contemplating these limitations is vital for cautious decision-making. The most typical limitations embody:
1. Further Complexities
Managing a number of tenants on a single useful resource requires added configuration. This consists of tenant onboarding, entry management, person authentication, and authorization. Lack of understanding and assist might result in undesirable outcomes like unintentional knowledge sharing or useful resource overhead.
To handle this, cautious planning and database assist ensures a safe person setting.
2. Safety Considerations
Malicious entry, unintentional misconfigurations, or vulnerabilities in underlying infrastructure can result in shared knowledge amongst tenants. As guardrails, implementing cautious design, conducting common audits, and incorporating multi-layer safety measures can strengthen general safety.
3. Efficiency Bottlenecks
Greater utilization of assets by a tenant can decelerate the efficiency of others. Shared indexing particularly impacts search efficiency as a result of runtime permission checks to match the entry record. Useful resource administration and management, common updates, and tenant training are vital to mitigate efficiency points.
4. System Outage
Scheduled upkeep, {hardware} failure, and software program bugs have an effect on all tenants after they share the same infrastructure. This results in knowledge, repute, and monetary losses. Common threat evaluation, infrastructure high quality assurance, and well timed backup can decrease the unfavourable affect of system outages.
Use instances of Multitenancy
Multitanency is beneficial in numerous functions, from e-commerce advice techniques to coaching giant machine studying (ML) fashions in corporations. A number of of the commonest use instances embody:
1. Suggestion Methods
Think about an e-commerce platform the place customers can join and save their procuring preferences. A multitenant setup will permit customized product suggestions to every person.
On the e-commerce platform, all tenants can set their standards, so the advice system sends customized product suggestions to finish customers.
2. Enterprise Functions
Massive software program functions serving a number of staff and clients use the identical database for all customers. All customers can add and handle their knowledge whereas defending it from others. For example, Dropbox and HubSpot permit all customers to share the identical assets however hold their knowledge shielded from one another.
3. Anomaly and Fraud Detection
Multitenancy permits the event of strong fraud detection techniques whereas holding particular person knowledge safe. Firms practice fraud detection fashions on their anonymized knowledge and ship solely the educated mannequin over the centralized database. This permits them to maintain their knowledge safe whereas contributing to growing fraud detection techniques.
For instance, credit card fraud detection systems use ML for enhanced privateness and effectivity.
When to Use and When To not Use Multitenancy
A number of elements contribute to the choice to modify to multitenancy, together with tenant efficiency, isolation necessities, and safety considerations. Let’s focus on when and when to not use multitenancy intimately beneath.
When to Use Multitenancy
The next indicators make multitenancy an excellent match:
- A number of tenants want separate environments.
- Tenants can settle for efficiency tradeoffs.
- Value discount is your precedence.
- Centralized tenant administration improves your operations.
When To not Use Multitenancy
Limitations of multitenancy hold it from making an excellent match for all conditions. A multitenant vector database isn’t an excellent match for you if you happen to’ve the next necessities:
- Tenants personal extremely delicate knowledge with strict safety necessities.
- A restricted variety of tenants with gradual progress.
- Tenants require devoted environments and may’t tolerate efficiency degradation.
- Restricted multitenant experience and functionality to deal with rising complexity.
Multitenancy introduces further scalability and manageability to the vector databases. If configured accurately, multitenancy saves important prices and assets for a corporation.
Keen on extra AI-related content material? Communicate with unite.ai.



Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.