Researchers from France have devised a way for figuring out newly-registered domains which might be probably for use in a ‘hit and run’ vogue by high-volume e mail spammers – typically, even earlier than the spammers have despatched out one undesirable e mail.
The method is predicated on evaluation of the best way that that the Sender Coverage Framework (SPF), a way of verifying e mail provenance, has been arrange on newly-registered domains.
Because of using passive DNS (Area Title System) sensors, the researchers have been in a position to get hold of close to real-time DNS information from Seattle-based firm Farsight, yielding SPF exercise for TXT records for a spread of domains.
Utilizing a category weight algorithm initially designed for processing imbalanced medical information, and applied within the scikit-learn machine studying Python library, the researchers have been in a position to detect three quarters of the pending spam domains inside moments, and even upfront of their operation.
The paper states:
‘With a single request to the TXT report, we detect 75% of the spam domains, presumably earlier than the beginning of the spam marketing campaign. Thus, our scheme brings necessary velocity of response: we are able to detect spammers with good efficiency even earlier than any mail is shipped and earlier than a spike within the DNS site visitors.’
The researchers declare that the options used of their method could possibly be added to current spam detection methods to extend efficiency, and with out including important computation overhead, because the system depends on SPF information passively inferred from close to real-time DNS feeds which might be already in use for various approaches to the issue.
The paper is titled Early Detection of Spam Domains with Passive DNS and SPF, and comes from three researchers on the College of Grenoble.
SPF Exercise
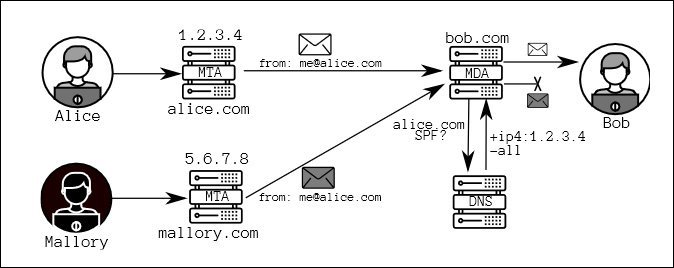
SPF is designed to keep away from the spoofing of e mail addresses, by verifying {that a} registered and licensed IP tackle has been used to ship an e mail.

On this instance of SPF, ‘Alice’ sends a benign e mail to ‘Bob’, whereas the attacker ‘Mallory’ tries to impersonate Alice. Each are sending mail from their very own domains, however solely Alice’s server is registered to ship Alice’s mail, so Mallory’s spoof is thwarted when his faux mail fails SPF verification. Supply: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.01932.pdf
Different strategies of e mail verification embrace DomainKeys Recognized Mail (DKIM) Signatures, and Area-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC).
All three strategies have to be registered as TXT data (configuration settings) on the area registrar for the genuine sending area.
Spam and Burn
Spammers exhibit ‘signature conduct’ on this regard. Their intention (or, at the very least, the collateral impact of their actions) is to ‘burn’ the popularity of the area and its IP addresses by blasting out bulk mail till both motion is taken by the community suppliers promoting these providers; or the related IP addresses are registered with well-liked spam-filter lists, making them ineffective for the present sender (and problematic for the long run homeowners of the IP addresses).

A slim window of alternative: the time, in hours, earlier than a brand new spam area is banned and made ineffective by SpamHaus and numerous different monitoring providers.
When the area location is now not practicable, the spammers transfer on to different domains and providers as crucial, repeating the process with new IP addresses and configurations.
Information and Strategies
The domains studied for the analysis cowl the time interval between Could and August of 2021, as supplied by Farsight. Solely freshly registered domains have been thought of, since this accords with the modus operandi of the persistent spammer.
The area listing was constructed over information from the ICANN Central Zone Information Service (CZDS). Blacklist info from the SURBL and SpamHaus initiatives was used to impact close to real-time identification of probably problematic new area registrations – although the authors concede that the imperfect nature of spam lists can result in benign domains unintentionally being categorized as potential sources of bulk mail.
After capturing DNS TXT queries to the newly registered domains discovered within the passive DNS feed, solely queries with legitimate SPF information have been retained, offering the bottom fact for the algorithms.

SPF has a lot of usable options; the brand new paper has discovered that whereas ‘benign’ area homeowners mostly use the +embrace mechanism, spammers have the best utilization of the (now deprecated) +ptr feature.

SPF rule utilization of spammers, in comparison with normal utilization.
A +ptr lookup compares the IP tackle of the sending mail to no matter data exist for an affiliation between that IP and the hostname (i.e. GoDaddy). If the hostname is found, its area is in comparison with the one which was first used to reference the SPF report.
Spammers can exploit the obvious rigor of +ptr to current themselves in a extra credible mild, when in truth the sources wanted to conduct at-scale +ptr lookups trigger many suppliers to skip the verify fully.
Briefly, the best way that spammers use SPF so as to safe a window of alternative earlier than the ‘blast and burn’ operation begins, represents a attribute signature that may be inferred by machine evaluation.

Attribute SPF relationships for spam domains.
Since spammers typically transfer to very close by IP ranges and sources, the researchers developed a relationship graph to discover the correlation between IP ranges and domains. The graph could be up to date nearly in actual time in response to new information from SpamHaus and different sources, turning into extra helpful and full over the course of time.
The researchers state:
‘The research of those buildings can spotlight potential spam domains. In our dataset, we discovered [structures] through which dozens of domains used the identical [SPF] rule and the vast majority of them appeared on spam blacklists. As such, it’s cheap to imagine that the remaining domains are more likely to haven’t but been detected or usually are not but energetic spam domains.’
Outcomes
The researchers in contrast the spam area detection latency of their method to SpamHaus and SURBL over a 50-hour interval. They report that for 70% of the spam domains recognized, their very own system was sooner, although conceding that 26% of the recognized spam domains did seem within the industrial blacklists within the following hour. 30% of the domains have been already in a blacklist once they appeared within the passive DNS feed.
The authors declare an F1 rating of 79% towards floor fact primarily based on a single DNS question, whereas competing strategies comparable to Exposure can require per week of preliminary evaluation.
They observe:
‘Our scheme could be utilized at early phases of a website life cycle: utilizing passive (or energetic) DNS, we are able to get hold of SPF guidelines for newly registered domains and classify them instantly, or wait till we detect TXT queries to that area and refine the classification utilizing hard-to-evade temporal options.’
And proceed:
‘[Our] finest classifier detects 85% of spam domains whereas holding a False Optimistic Price below 1%. The detection outcomes are outstanding on condition that the classification solely makes use of the content material of the area SPF guidelines and their relationships, and arduous to evade options primarily based on DNS site visitors.
‘The efficiency of the classifiers stays excessive, even when they’re solely given the static options that may be gathered from a single TXT question (noticed passively or actively queried).’
To see a presentation on the brand new methodology, take a look at the embedded video under:
First printed fifth Could 2022.