Unhealthy information if you wish to transfer to the moon or Mars: housing is a little bit onerous to return by. Luckily, NASA (as at all times) is considering forward, and has simply proven off a self-assembling robotic construction that may simply be a vital a part of shifting off-planet.
Published today in Science Robotics, the paper from NASA Ames Analysis Heart describes the creation and testing of what they name “self-reprogrammable mechanical metamaterials,” which is a extremely exact method to describe a constructing that builds itself. The inevitable acronym for it’s “Automated Reconfigurable Mission Adaptive Digital Meeting Techniques,” or ARMADAS.
“We predict such a development expertise can serve lots of very basic functions,” lead creator Christine Gregg informed TechCrunch. “Within the close to time period, the strong autonomy and light-weight buildings of our strategy strongly profit functions in austere environments, just like the lunar floor or area. This consists of lunar floor development of communication towers and shelters, which shall be wanted earlier than astronauts arrive, in addition to on-orbit buildings like booms and antennas.”
The fundamental concept of the self-building construction is in a intelligent synergy between the constructing materials — cuboctahedral frames they name voxels — and the 2 kinds of robots that assemble them.
One kind of robotic walks alongside the floor with two legs, seemingly impressed by our personal biology’s kinesin transport molecules, carrying a voxel like a backpack. When that’s put in place, a fastening robotic that lives within the body itself like a worm slithers over and tightens the reversible attachment factors. Neither one wants a robust sensing system, and the best way they work means excessive precision will not be required both.
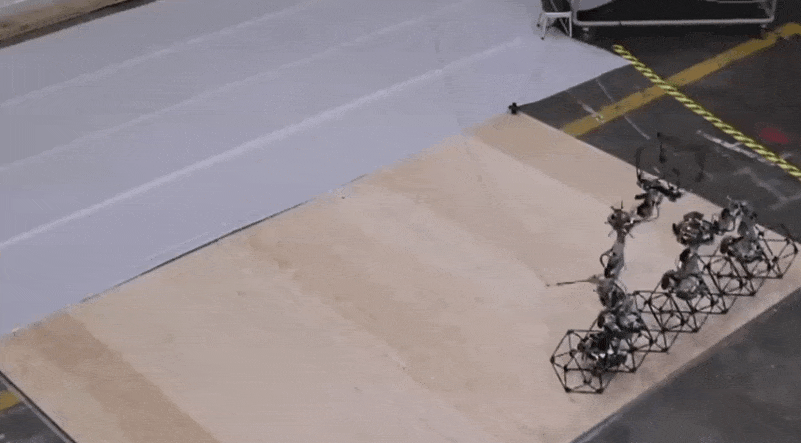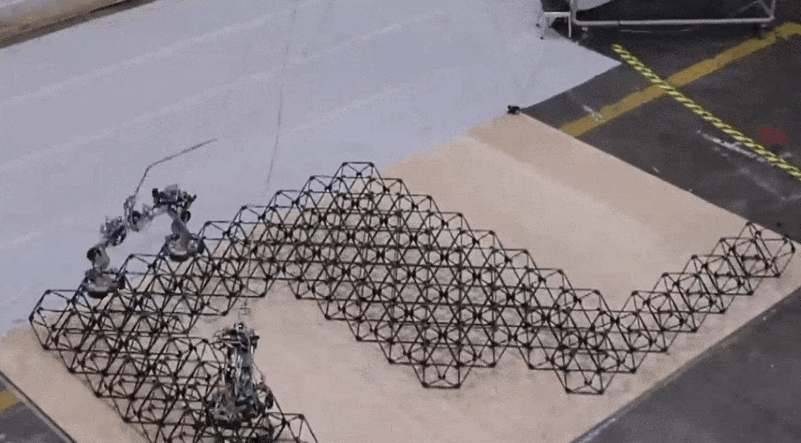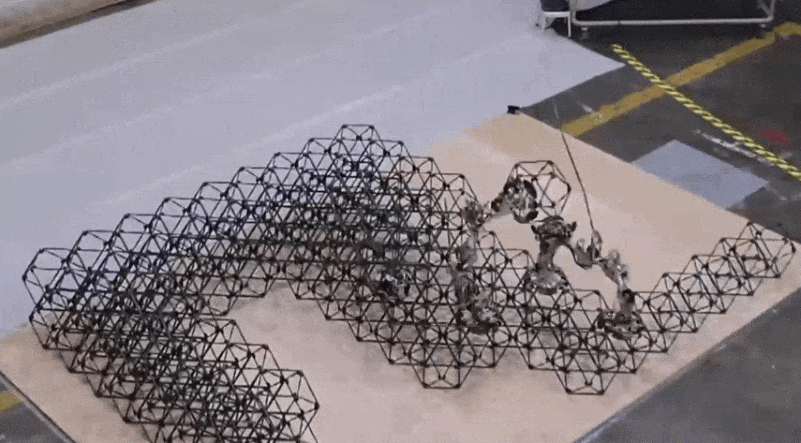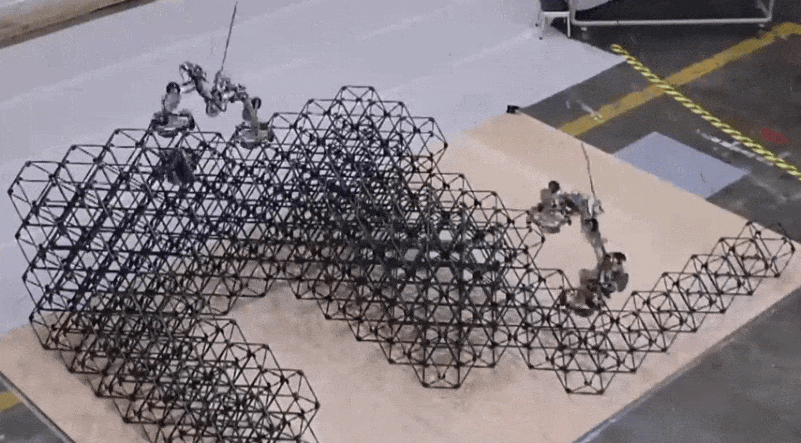
You possibly can see a pair of walkers and a fastener worm in many of the photos on this submit. And right here’s a transport walker handing off a voxel to a placement walker, with the fastener bot lurking under ready to go over and lock the body into place.
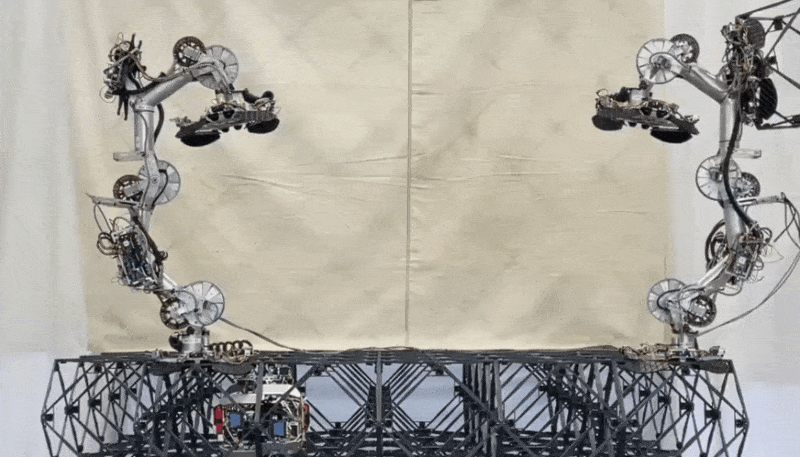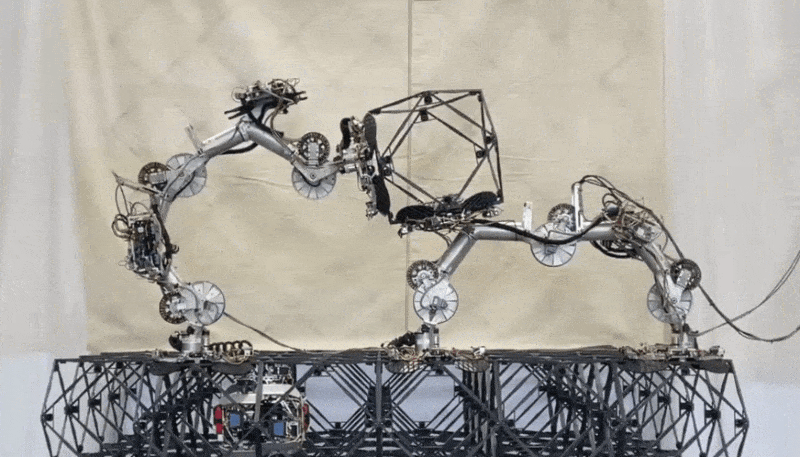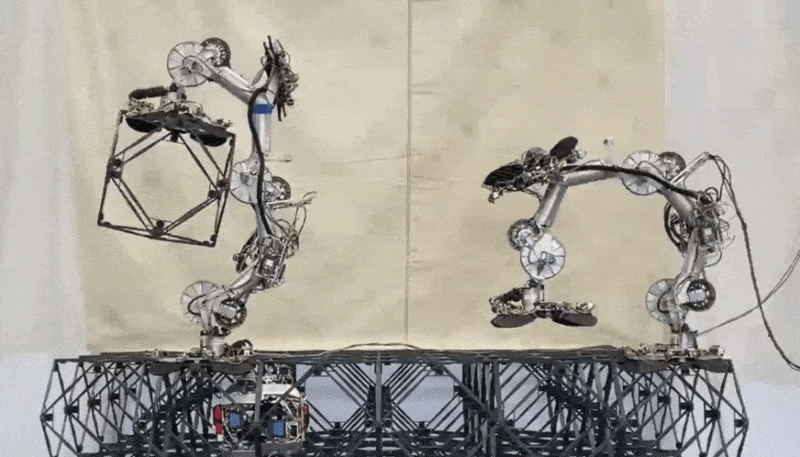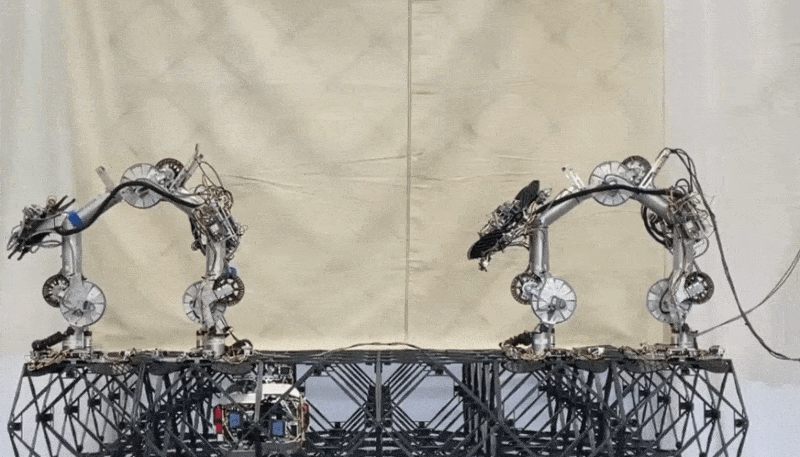
Two robots change a structural factor whereas a 3rd waits under to affix it to the lattice. Picture Credit: NASA
The form of the items permits them to be hooked up at varied angles whereas sustaining good construction power. You most likely wouldn’t need to retailer rocks on prime of a dome made out of these items, however they’d be glorious as a base on which so as to add insulation and sealant to make a dwelling.
“We predict such a development is especially suited to lengthy length and/or very giant infrastructure, together with habitats, instrumentation or another infrastructure on orbit or the floor of the moon (utility towers, automobile touchdown amenities),” mentioned co-author Kenneth Cheung. “For us, the buildings and all the robotic methods are assets that may be optimized over area and time. It appears to be like like there’ll at all times be conditions the place the optimum factor is to depart simply construction in place (and maybe go to to examine it with a robotic periodically), so we began with that.”
The items themselves may be constructed on-site, Gregg famous:
“The voxels will be constructed from many various supplies and manufacturing processes. Ultimately, for area functions, we want to make voxels from supplies we discover in situ on the moon or different planetary our bodies.”
In fact, these movies of the robots at work are extremely accelerated, however not like work in a manufacturing unit or sidewalk, pace isn’t essentially of the essence in terms of constructing stuff in area or on the floor of one other planet.
“Our robots can work quicker than proven on this paper, however we didn’t see it as essential to the first objectives to make them accomplish that. Basically, the best way to make this technique work quicker is to make use of extra robots,” mentioned Cheung. “The general technique for scalability (of pace, measurement) is to have the ability to push the complexity of scale onto algorithms, for planning and scheduling in addition to detecting faults and performing repairs.”
The robots developed by the lab took 256 voxels and assembled them right into a satisfactory shelter construction throughout a complete of 4.2 days of labor. Right here’s what the beginning of that regarded like (once more, nowhere close to actual time):
Picture Credit: NASA
If we’d despatched them forward to Mars or the moon a 12 months forward of a crew, they may construct a dozen such buildings twice the scale with time to spare. Or maybe they may affix the required plating to the surface afterwards and seal it up — that’s quite past the scope of the paper printed at the moment, however an apparent subsequent step.
Although the robots have tethers working energy to them on this lab setting, they’re being designed with battery operation or on-site energy in thoughts. The fastener bot is already battery-powered, and the researchers are contemplating methods of retaining the walkers charged between and even throughout operations.
“We envision robots might be autonomously recharged at energy stations and even maybe beamed energy wirelessly. As you talked about, energy may be routed by the construction itself, which could be helpful for outfitting the construction in addition to powering the robots,” Gregg mentioned.
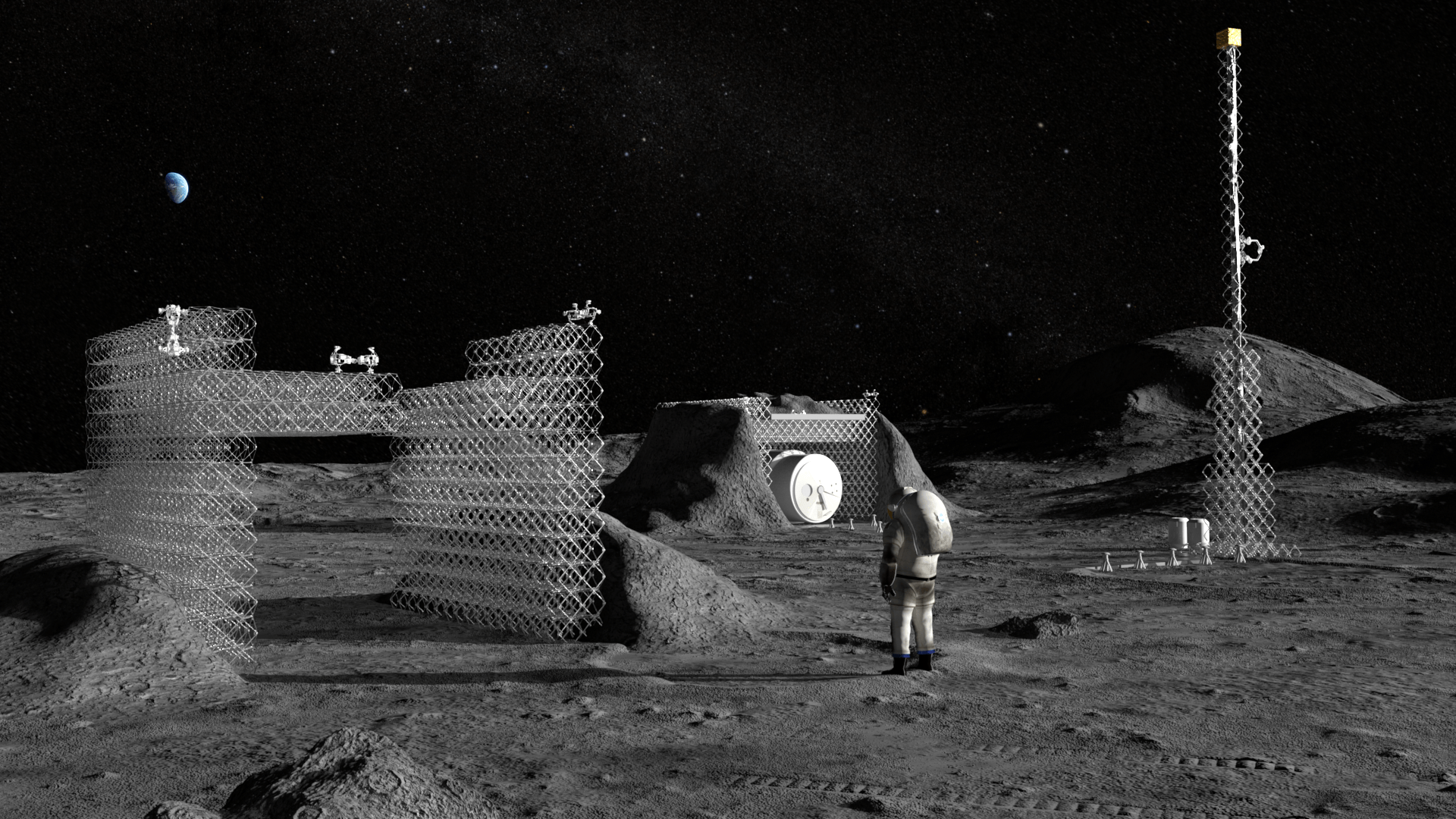

Idea illustration of ARMADAS constructing underneath astronaut supervision. Picture Credit: NASA
Variations of the robotic have already flown in area and accomplished work in microgravity, so no worries on that rating. And there’s nothing in precept stopping them from working in non-Earth gravities just like the moon’s. That mentioned, that is solely the start — like revealing the existence of 2x4s and nails. There’s extra on the potential, and idea illustrations of what they may construct, at this NASA news post.
“The subsequent variations of our robots for the laboratory setting shall be quicker and extra dependable, primarily based on our classes discovered with the primary variations. We’re very concerned about understanding how several types of constructing blocks will be built-in into the buildings to offer practical outfitting,” Gregg mentioned.
Likewise analysis will proceed on buildings using swarms of robots, not only a handful; a crude shelter would possibly take two walkers 4 days, however one thing 10 instances greater would possibly take 100 instances longer. However many arms — particularly robotic ones — make mild work.
